3D scanning and printing play a key role in quality control, design, and inspection procedures. It is a measuring non-contact technology that transforms physical objects into digital 3D CAD models (Computer-Aided Design). Today, this scanning technology has become an indispensable tool for manufacturers who require precise dimensional inspection. Below are some tips for effectively utilizing 3D scanning to build top-quality finished products.
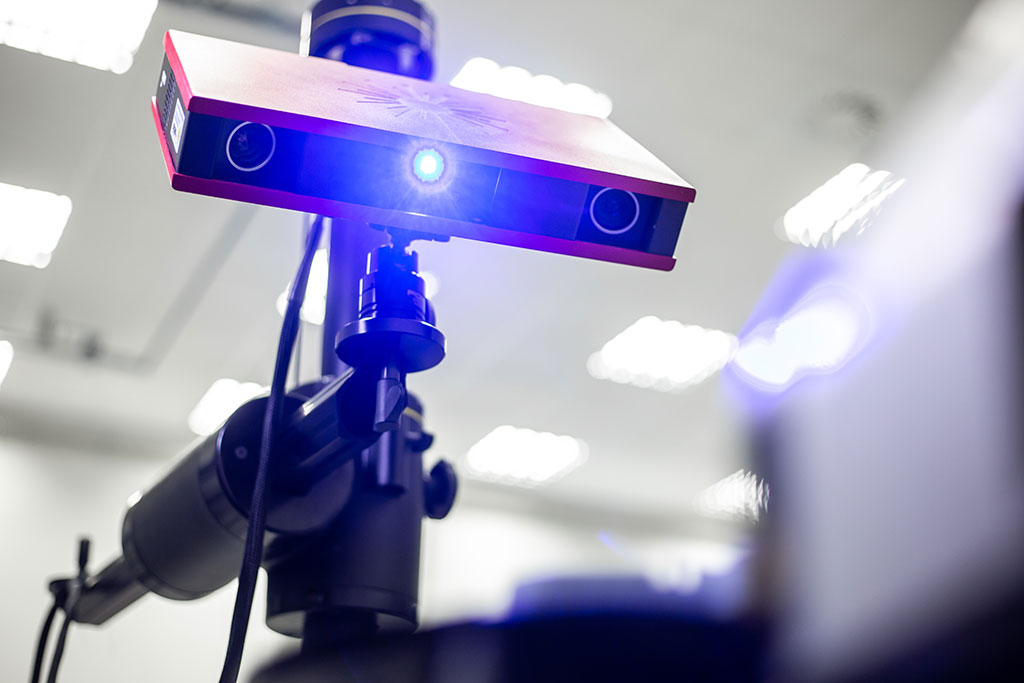

How 3D Scanning Works
Three-dimensional scans recreate data digitally based on an object’s physical characteristics. In addition, there are various 3D scanning methods which include CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), light scanners, laser scanners, and CT (Computed tomography) scanners. All of these 3D scanning tools collect raw data in the form of point clouds and subsequently transform them into user-friendly mesh formats such as STL and OBJ files that can be used for reverse engineering to create CAD data.
Applying 3D Scanning to Product Creation
Design engineers turn to 3D scanning to increase production speed and decision-making processes. For instance, traditional contact measuring systems like standard monitoring equipment and hand instruments only analyze a single data point concurrently, which makes them both repetitive and time-consuming.
Laser scans, on the other hand, use lasers that travel across an object’s surface. Each scan can be completed within hours, depending on the object’s size. 3D scanners are routinely used in the film and computer game industries to construct 3D models. Scanning objects made in the real world is simpler than building it from scratch within 3D modeling software.
3D scans can be used to inform jewelers of whether or not a jewel will fit within a specific bracelet or pendant. Structured Light based 3D scans are highly accurate for producing merchandise with precise functionalities. By projecting a pattern of white light on the surface they are able to capture a highly detailed and accurate representation of the object.
Increased Customization
Product customization is extremely important. The merger of 3D printing and 3D scanning has enabled item archetypes without requiring traditional plaster casting. Blue light 3D scanners can measure parts with incredible resolution and speed. Because it is non-contact-based technology, users do not require any specific programming skills while scanning.
Reverse Engineering
Product developers to reverse engineer an existing product will find 3D scanners handy. This is because different sized objects can be scanned with exacting measurements, which can subsequently be used for analysis, 3D printing, and 3D modeling.
Today, developing prototypes have become increasingly easy due to the speed of 3D scanners. Both blue and white light scanners are simpler and safer to operate since they have the support of superior software and FOV lenses. One of the primary benefits of using 3D scanning is lowering the number of prototype-based cycles. A necessity to have between the design and production phases. These scanners will scan cross-sections while storing every bit of data related to the scan.