3D scanning is all about capturing the physical size and shape of an object and transferring that into the digital world. Details captured include the colorized texture and complex geometry of the object. From there, the 3D file can be edited or printed to the user’s specificities. Usually, more than one scan is required to capture the object from a multitude of angels. If you are wondering how to choose the right 3D scanning device to suit your needs, we share more with you in this article!

Laser 3D Scanners
This type of scanner makes use of trigonometric triangulation by projecting one or more laser lines onto the object and capturing its reflection through the use of sensors. Laser scanners are highly popular because of their portability and they are particularly useful for scanning tough surfaces, such as dark and shiny finishes. Some applications of laser scanners include part inspection and information modeling.
White Light 3D Scanners
White light 3D scanners are typically mounted on a tripod, although there are also handheld versions. They work by projecting a grid of light over the part being scanned. Once the part has been scanned, the grid is modified and sensors are used to calculate the object’s 3D shape. White light scanners are most commonly used for reverse engineering and inspection purposes.
Medium and Long Range 3D Scanners
As implied by its name, long range 3D scanners are most suitable for scanning large objects such as buildings and vehicles, including aircraft. These scanners capture millions of points by directing the laser(s) outwards towards the object and rotating 360 degrees.
These scanners come in two main types:
- Pulse range, which is suitable for scanning objects the size of industrial equipment and automobiles
- Phase shift, which additionally modifies the power of the laser beam
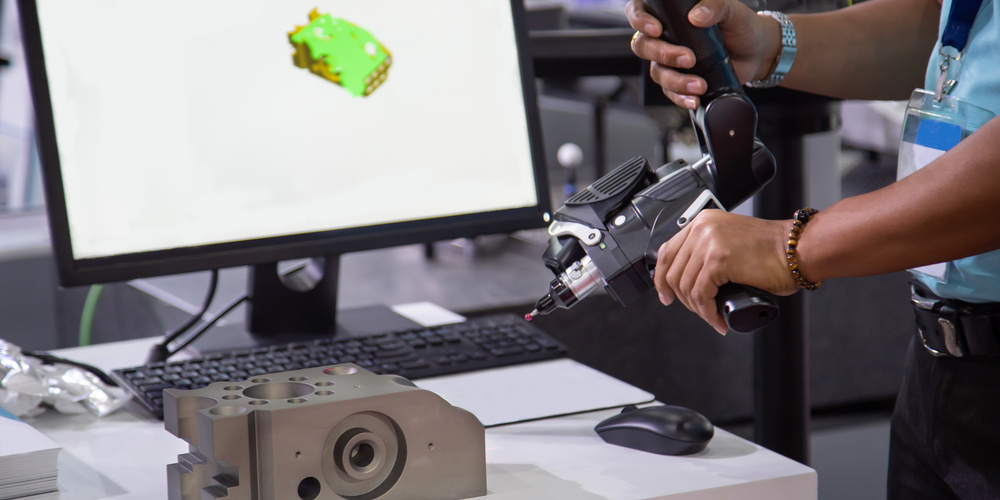
Contact Scanning
This method of scanning makes use of a probe applied to the surface of the object. The probe is moved all over the object, which is held still, in order to capture all its details and create a digital file. Because contact scanning involves physical contact with the object, even reflective and transparent objects can be scanned using this method, which is also one of its most common applications.
Photogrammetry
With photogrammetry technology, all you need to do is take photos of an object from multiple angles. This can be done using a camera or even your smartphone while specific settings are enabled. From there, these photos are stitched together by special software, which identifies the pixels corresponding to each physical point and brings them together. Some applications of photogrammetry include land surveying, drone photography, and creating maps out of aerial photos.
Choosing the Right 3D Scanning Method for Your Industrial Needs
Now that you know more about the different types of 3D scanning devices out there, you may still be unsure which is most suitable for your purposes. When you engage our services at Kemperle Industries, our expert team can make the best recommendation for you.